Buffer. a chemical solution that keeps pH within normal limits by absorbing excess hydrogen, or H+, ions and hydroxide, or OH-, ions.
Hence, What is a buffer pH?
The buffer pH is a measure of the residual or reserve soil acidity — the soil acidity that is neutralized by lime in order to raise the pH. In general, the change in buffer pH determines how much lime is needed to change the pH to the desired level (based on the crops being grown).
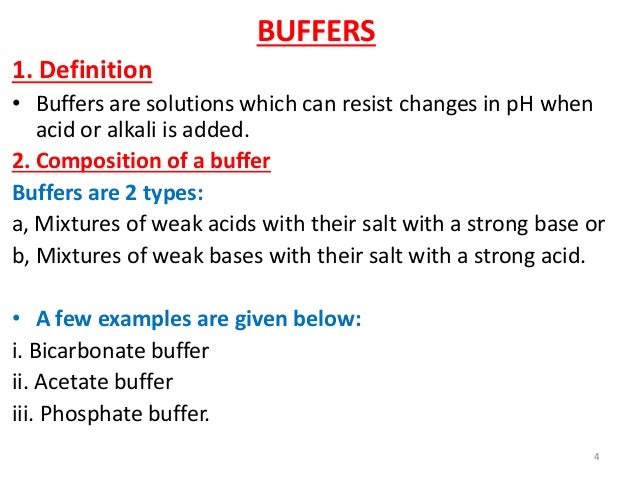
Consequently, What is a buffer and why is it useful to cells? Buffers are chemicals that help a liquid resist changing its acidic properties when other chemicals are added that will normally cause a change in these properties. Buffers are essential for living cells. This is because buffers maintain the right pH of a liquid.
What is a buffer quizlet? What is the definition of a buffer? A solution of a weak acid (proton donor) and its conjugated base (proton acceptor) that resists significant changes in pH upon addtion of small quantites of strong acid or base.
In addition, What is the purpose of the buffer quizlet? The function of a buffer is to resist changes in the pH of a solution when acid (HCl) or base (NaOH) (small amount) is added.
Why is a buffer important?
A buffer is a chemical substance that helps maintain a relatively constant pH in a solution, even in the face of addition of acids or bases. Buffering is important in living systems as a means of maintaining a fairly constant internal environment, also known as homeostasis.
How do buffers work?
A buffer is simply a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. Buffers work by reacting with any added acid or base to control the pH.
What is difference between pH and buffer pH?
pH is a fundamental scale that we use in chemistry to measure the acidity r basicity of a solution. Buffers are chemical solutions that can resist the changes in pH. Therefore, the difference between pH and buffer is that the pH is a logarithmic scale whereas a buffer is an aqueous solution.
How does a buffer work?
How do buffers work? Buffers work by neutralizing any added acid (H+ ions) or base (OH- ions) to maintain the moderate pH, making them a weaker acid or base.
Can amino acids function as buffers?
An amino acid can act as a buffer because it can react with added acids as well as to keep the pH nearly constant. Because an amino acid has both an acidic group which is a carboxyl group and a basic group which is an amine group, hence it can act as both acid and as a base therefore amino acids can act as a buffer.
What is the pH range of most buffer systems?
Buffers are generally good over the range pH = pKa ± 1. The ammonia buffer would be effective between pH = 8.24 – 10.24. The acetate buffer would be effective of the pH range from about 3.74 to 5.74. Outside of these ranges, the solution can no longer resist changes in pH by added strong acids or bases.
How do buffers work?
How do buffers work? Buffers work by neutralizing any added acid (H+ ions) or base (OH- ions) to maintain the moderate pH, making them a weaker acid or base.
In what way is a buffer important to living things?
In living organisms, buffers are important because they resist sudden changes in the pH of body fluids of living organisms: Bicarbonate buffer maintains the pH of the blood. Phosphate buffer maintains the internal environment of cells. Hemoglobin has buffering capacity.
What is a buffer made from?
Buffers can be made from weak acids or base and their salts. For example, if 12.21 grams of solid sodium benzoate are dissolved in 1.00 L 0.100 M benzoic acid (C6H5COOH, pKa = 4.19) solution, a buffer with a pH of 4.19 will result: Buffers can be made from two salts that provide a conjugate acid-base pair.
What are the buffers in the human body?
The three major buffer systems of our body are carbonic acid bicarbonate buffer system, phosphate buffer system and protein buffer system.
What is a buffer made of?
A buffer is made by mixing a large volume of a weak acid or weak base together with its conjugate. A weak acid and its conjugate base can remain in solution without neutralizing each other. The same is true for a weak base and its conjugate acid.
What is buffer and its types?
Buffers are broadly divided into two types – acidic and alkaline buffer solutions. Acidic buffers are solutions that have a pH below 7 and contain a weak acid and one of its salts. For example, a mixture of acetic acid and sodium acetate acts as a buffer solution with a pH of about 4.75.
How does a buffer maintain pH?
Maintaining the proper pH is critical for the chemical reactions; hence buffers are used. Buffer is the combination of a weak acid and the weak base. Hence when dissociated, H+ and OH- ions are released, which helps to stop the massive changes in pH levels and aids to maintain the balance.
Do buffers increase or decrease pH?
“A buffer is an aqueous solution that resists changes in pH upon the addition of an acid or a base”. Also, adding water to a buffer or allowing water to evaporate from the buffer does not change the pH of a buffer significantly.
What is buffer value?
The value indicating the capability of a substance in solution to absorb acid or alkali without changing the pH.
What is the relationship between pH and buffer solution?
Key Points. A basic solution will have a pH above 7.0, while an acidic solution will have a pH below 7.0. Buffers are solutions that contain a weak acid and its a conjugate base; as such, they can absorb excess H+ions or OH– ions, thereby maintaining an overall steady pH in the solution.
Can proteins act as buffers?
Nearly all proteins can function as buffers. Proteins are made up of amino acids, which contain positively charged amino groups and negatively charged carboxyl groups. The charged regions of these molecules can bind hydrogen and hydroxyl ions, and thus function as buffers.
What is hemoglobin buffer?
Hemoglobin as a Buffer
Hemoglobin is the principal protein inside of red blood cells and accounts for one-third of the mass of the cell. During the conversion of CO2 into bicarbonate, hydrogen ions liberated in the reaction are buffered by hemoglobin, which is reduced by the dissociation of oxygen.
Why are proteins not good buffers?
Indeed, when the pH buffer is equal to the pI (isoelectric point), the protein has no charge. Consequently, the protein is not able to bind to an ion exchange column (anion and cation).