MCG ( Master Cell Group ) Bearer. SCG ( Secondary Cell Group ) Bearer.
in the same way What is split bearer? Me: Split bearer is a function to allow the split of data going to gNB from the core side into two paths, the 1st path through the 5G air interface toward the UE and the 2nd one is toward X2 interface with the anchored eNB and then eNB will transfer this data through the 4G air interface to the UE.
What does en-DC stand for? So what is ENDC? ENDC stands for E-UTRAN New Radio – Dual Connectivity, in standards parlance. According to 3GPP standards documents, ENDC allows user equipment to connect to an LTE enodeB that acts as a master node and a 5G gnodeB that acts as a secondary node.
What is LTE anchor? At 5GNR NSA Option 3x (currently what is being used), you still need an anchor, a leg, PCELL, on LTE to allow 5G to be used, meaning, you are connected simultaneously on LTE and NR. This anchor, or leg, PCELL, is where all the control plane information goes, while on NR only user plane data.
What is e-utran in LTE?
(Evolved-UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network) E-UTRAN is the air interface in an LTE cellular network. Officially, E-UTRAN governs the base station, while E-UTRA (without the “N”) defines the mobile device side. E-UTRAN uses the OFDMA modulation method for the downlink and SC-FDMA for the uplink.
Beside this How many bearers are in 5G?
SRB stands for Signaling Radio Bearer.”Signalling Radio Bearers” (SRBs) are defined as Radio Bearers (RBs) that are used only for the transmission of RRC and NAS messages. As per 3GPP specification TS38. 331, Signalling radio bearers, there are four different types of SRB in 5G New Radio (NR) defined as follows.
How many DRB is 5G? For each UE, 5GC establishes one or more PDU sessions and 5G-RAN establishes at least one DRB together with PDU session. Additional DRBs are configured for QoS flows of that PDU session consecutively. 5G-RAN maps packets which belong to the different PDU sessions to different DRBs.
What is 5G dual connectivity? 5G NR Dual Connectivity (DC) is a feature that allows mobile devices to utilize both mid-band and mmWave frequencies (LTE and FR2) to provide improved network coverage and data rate. … Non-standalone 5G networks rely on an LTE core and radio access network with the addition of a 5G carrier.
Is ENDC same as NSA?
In short, ENDC is an NSA 5G architecture that allows smartphones to access both 5G and 4G LTE networks at the same time. A key benefit of ENDC is that it combines the bandwidth of 5G and 4G LTE, effectively allowing operators to take advantage of the benefits of both network technologies simultaneously.
What is 5G architecture? 5G Core Architecture
The new 5G core, as defined by 3GPP, utilizes cloud-aligned, service-based architecture (SBA) that spans across all 5G functions and interactions including authentication, security, session management and aggregation of traffic from end devices.
What is MME and HSS?
The MME is the key control-node for the LTE access-network. It is responsible for idle mode User Equipment (UE) paging and tagging procedure including retransmissions. … The MME also terminates the S6a interface towards the HSS for roaming UEs.
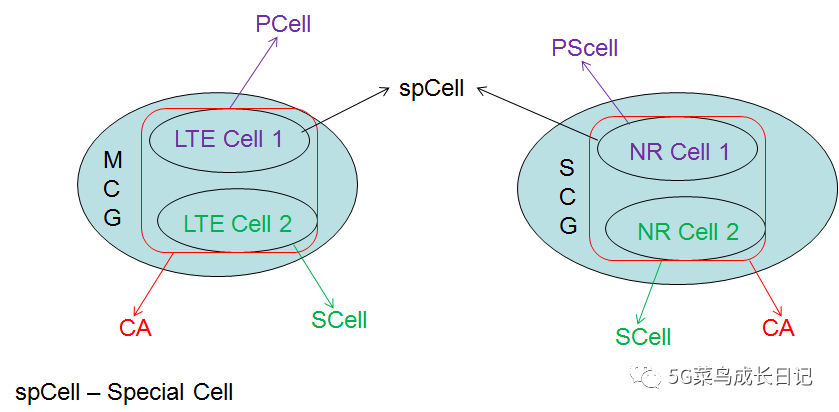
What is SCG and MCG? November 7, 2021. The MCG and the SCG are concepts in dual connectivity (DC, Dual connectivity). It may be simply understood that the MCG is located in a group in which a cell in which the UE first initiates random access (RACH) is located. If there is no dual link, there is no concept of MCG and SCG.
What is MCG and SCG in LTE?
In dual connectivity, a user equipment (UE) can simultaneously be connected to two cell groups called master cell group (MCG) and secondary cell group (SCG) through master eNB (MeNB) and secondary eNB (SeNB), respectively.
What is LTE rat?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. A Radio Access Technology or (RAT) is the underlying physical connection method for a radio based communication network. Many modern mobile phones support several RATs in one device such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and GSM, UMTS, LTE or 5G NR.
What is X2 interface? X2 interface. A point-to-point logical interface between two eNodeBs with the E-UTRAN. It supports the exchange of signaling information between two eNodeBs and supports the forwarding of protocol data units (PDUs) to the respective tunnel endpoints. X2 Application Protocol (X2AP) Protocol used by the X2 interface.
How many LTE bearers are there? The maximum of 11 still holds in 4G/LTE networks. Figure 1 shows the relationship between bearers and P-GWs.
What is MCG and SCG?
In dual connectivity, a user equipment (UE) can simultaneously be connected to two cell groups called master cell group (MCG) and secondary cell group (SCG) through master eNB (MeNB) and secondary eNB (SeNB), respectively.
What is master cell group? With respect to Dual Connectivity, MCG is the term given to the group of serving cells associated with the Master RAN node.
What is E-RAB?
An E-RAB (E-UTRAN Radio Access Bearer) refers to the concatenation of an S1 bearer and the corresponding radio bearer. When an E-RAB exists, there is a one-to-one mapping between this E-RAB and an EPS bearer of the Non Access Stratum.
What is DC mode? The term EN-DC (Evolved-Universal Terrestrial Radio Access-New Radio) refers to E-UTRA NR Dual connectivity. This feature allows mobile device to exchange data between itself and NR base station along with simultaneous connection with LTE base station.
What is DC in LTE?
Dual connectivity (DC) is a LTE Rel-12 feature for small cell enhancement. Similar to carrier aggregation (CA), it aims to utilize the radio resource within multiple carriers to improve UE throughput. … In CA implementation, user traffic is split between carriers in MAC; while in DC implementation, it is split in PDCP.
What’s a 5G phone? A: 5G is the 5th generation mobile network. … 5G wireless technology is meant to deliver higher multi-Gbps peak data speeds, ultra low latency, more reliability, massive network capacity, increased availability, and a more uniform user experience to more users.
Which 5G band will be used in India?
It is worth noting that each and every telecom operator including Reliance Jio, Vodafone Idea (Vi), and Bharti Airtel are testing their 5G networks in the 3.5 GHz spectrum allotted to them by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT).
What is the difference between 5G SA and 5G NSA? NSA does not have a 5G core network, and SA has a 5G core network, which is a key difference. … Under the NSA network, the terminal is dual-connected to two wireless access technologies, LTE and NR; under the SA network, the terminal is only connected to NR one wireless access technology.
Do’t forget to share this post !