MR-DC is the general term given to a range of different Dual Connectivity configuration options, largely associated with 5G. With MR-DC, the Master RAN Node functions as the controlling entity, utilizing a Secondary RAN for additional data capacity.
in the same way What are the multi RAT dual connectivity Mr-DC types supported with 5GC? MR-DC with the 5GC
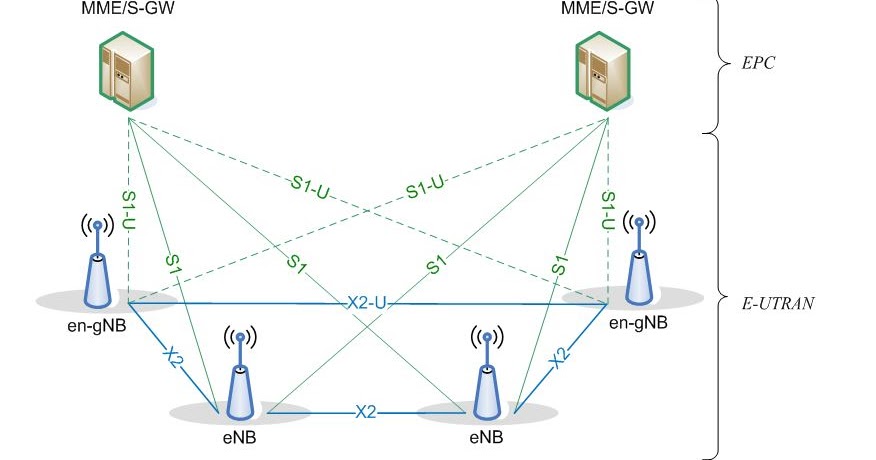
- E-UTRA-NR Dual Connectivity. NG-RAN supports NG-RAN E-UTRA-NR Dual Connectivity (NGEN-DC), in which a UE is connected to one ng-eNB that acts as an MN and one gNB that acts as an SN. …
- NR-E-UTRA Dual Connectivity. …
- NR-NR Dual Connectivity.
What is MCG and SCG in 5G? MCG ( Master Cell Group ) Bearer. SCG ( Secondary Cell Group ) Bearer.
What is the difference between gNB and Ng-eNB? gNB is the 5G radio base station, whereas ng-eNB is an upgraded version of the 4G LTE base station. 5G networks use a radio technology called New Radio – NR. 5G NR and 4G LTE networks will co-exist for a long time to cater to a wide range of customer use cases.
What does en-DC stand for?
So what is ENDC? ENDC stands for E-UTRAN New Radio – Dual Connectivity, in standards parlance. According to 3GPP standards documents, ENDC allows user equipment to connect to an LTE enodeB that acts as a master node and a 5G gnodeB that acts as a secondary node.
Beside this What is EPS bearer?
EPS bearer is a combination of several sub bearers which are E-RAB bearer, Radio bearer, S1 bearer, S5 bearer and S8 bearer: E-RAB bearer: transports the packets of an EPS bearer between UE and SGW. … External bearer: transports the user packets between PGW and external networks.
What is LTE anchor? At 5GNR NSA Option 3x (currently what is being used), you still need an anchor, a leg, PCELL, on LTE to allow 5G to be used, meaning, you are connected simultaneously on LTE and NR. This anchor, or leg, PCELL, is where all the control plane information goes, while on NR only user plane data.
What is the difference between BSC and RNC? Q: What is the difference between a BSC and RNC
A: The BSC is the Base Station Control used in the 2G cellular system. It is responsible for the control of Base Transceiver Stations (BTS) in a telecommunication system, while the RNC is used in the third generation telecommunication system.
What is 3G RNC?
The Radio Network Controller (RNC) is a governing element in the UMTS radio access network (UTRAN) and is responsible for controlling the Node Bs that are connected to it.
What is G in gNB? In gNB, the letter “g” stands for next generation. The term nNB was deemed confusing and ngNB was not desirable as only a single letter in front of NB was required. In summary, the gNB handles radio communications with the 5G capable UE using the 5G NR (New Radio) air interface.
Is ENDC same as NSA?
In short, ENDC is an NSA 5G architecture that allows smartphones to access both 5G and 4G LTE networks at the same time. A key benefit of ENDC is that it combines the bandwidth of 5G and 4G LTE, effectively allowing operators to take advantage of the benefits of both network technologies simultaneously.
What is 5G architecture? 5G Core Architecture
The new 5G core, as defined by 3GPP, utilizes cloud-aligned, service-based architecture (SBA) that spans across all 5G functions and interactions including authentication, security, session management and aggregation of traffic from end devices.
What is 5G dual connectivity?
5G NR Dual Connectivity (DC) is a feature that allows mobile devices to utilize both mid-band and mmWave frequencies (LTE and FR2) to provide improved network coverage and data rate. … Non-standalone 5G networks rely on an LTE core and radio access network with the addition of a 5G carrier.
How many LTE bearers are there?
The maximum of 11 still holds in 4G/LTE networks. Figure 1 shows the relationship between bearers and P-GWs.
What is 4G EPS? The LTE network called EPS (Evolved Packet System) is an end-to-end (E2E) all IP network; EPS is divided into two parts – LTE part which deals with the technology related to a radio access network (E-UTRAN) and EPC part which deals with the technology related to a core network.
What is LTE handover? Abstract: Handover in LTE occurs when a device moves from the cell coverage serving it towards another; a process where the user established session must not be interrupted due to this cell change.
What is MME and HSS?
The MME is the key control-node for the LTE access-network. It is responsible for idle mode User Equipment (UE) paging and tagging procedure including retransmissions. … The MME also terminates the S6a interface towards the HSS for roaming UEs.
What is SCG and MCG? November 7, 2021. The MCG and the SCG are concepts in dual connectivity (DC, Dual connectivity). It may be simply understood that the MCG is located in a group in which a cell in which the UE first initiates random access (RACH) is located. If there is no dual link, there is no concept of MCG and SCG.
What is MCG and SCG in LTE?
In dual connectivity, a user equipment (UE) can simultaneously be connected to two cell groups called master cell group (MCG) and secondary cell group (SCG) through master eNB (MeNB) and secondary eNB (SeNB), respectively.
What is BTS Telecom? A base transceiver station (BTS) is a fixed radio transceiver in any mobile network. … It sends and receives radio signals to mobile devices and converts them to digital signals that it passes on the network to route to other terminals in the network or to the Internet.
How can a BTS be linked to BSC?
The BSC controls the activities of the BTS. The BSC is referred to as a mediator and physical link between the BTS and the Mobile Switching Center (MSC). It allocates radio channels, receives measurement from mobile devices, controls BTS to BTS handover and call setup.
How are BTS and BSC connected? The BTS and the BSC communicate across the specified Abis interface, enabling operations between components that are made by different suppliers. … The BSS uses the Abis interface between the BTS and the BSC. A separate high-speed line (T1 or E1) is then connected from the BSS to the Mobile MSC.
What is IuPS and IuCS?
IuPS interface works between the UMTS RNC (Radio Network Controller) and the SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node) supporting UMTS integrated services such as multimedia and global roaming to mobile users. IuCS interface in UMTS links the RNC (Radio Network Controller) with a 3G MSC (3G Mobile Switching Centre).
What is BSC in telecom? A base station controller (BSC) is a network element that controls and monitors a number of base stations and provides the interface between the cell sites and the mobile switching center (MSC).
What is Node B Telecom?
Node B is the telecommunications node in particular mobile communication networks, namely those that adhere to the UMTS standard. The Node B provides the connection between mobile phones (UEs) and the wider telephone network. … Node B corresponds to BTS (base transceiver station) in GSM.
Do’t forget to share this post !