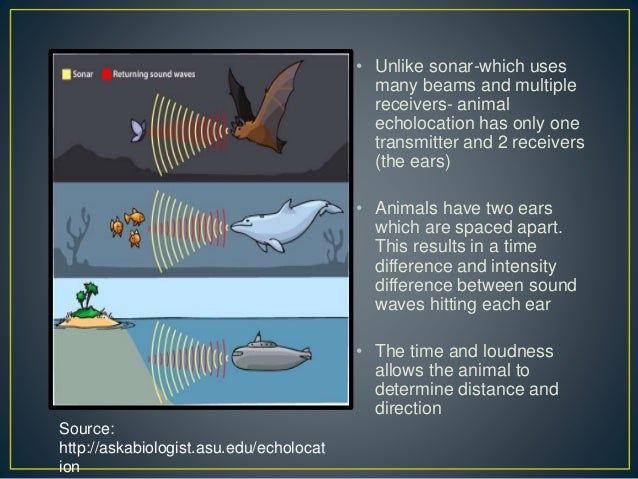
SONAR – Sound Navigation And Ranging, is the process of listening to specific sounds to determine where objects are located. Echolocation – A method used to detect objects by producing a specific sound and listening for its echo.
in the same way What is the history of echolocation? The term echolocation was coined in 1938 by the American zoologist Donald Griffin, who, with Robert Galambos, first demonstrated the phenomenon in bats. … In 1912, the inventor Hiram Maxim independently proposed that bats used sound below the human auditory range to avoid obstacles.
What is causes an echo? Echoes. An echo is a sound that is repeated because the sound waves are reflected back. Sound waves can bounce off smooth, hard objects in the same way as a rubber ball bounces off the ground. … Echoes can be heard in small spaces with hard walls, like wells, or where there are lots of hard surfaces all around.
What is dolphin echolocation? Dolphins and other toothed whales locate food and other objects in the ocean through echolocation. In echolocating, they produce short broad-spectrum burst-pulses that sound to us like “clicks.” These “clicks” are reflected from objects of interest to the whale and provide information to the whale on food sources.
Is echolocation a radar?
Just like bat echolocation, sonar uses sound waves to navigate and determine the location of objects like submarines and ships. … Radar uses electromagnetic waves to determine the location of objects like planes and ships. Like bat echolocation, radar is also used on open air.
Beside this Do all bats echolocate?
All bats — apart from the fruit bats of the family Pteropodidae (also called flying foxes) — can “echolocate” by using high-pitched sounds to navigate at night.
Why do bats echolocate? Bats use echolocation to navigate and find food in the dark. To echolocate, bats send out sound waves from the mouth or nose. When the sound waves hit an object they produce echoes. … Echolocation allows bats to find insects the size of mosquitoes, which many bats like to eat.
What are 3 examples of echolocation? This is known as echolocation.
- Bats. Bats emit pulses of high-pitched sounds — beyond the range of human hearing — and then listen for the echoes that are produced when these sound waves bounce off objects around them. …
- Whales and Dolphins. …
- Oilbirds and Swiftlets. …
- Shrews. …
- Humans.
Why is sound clearer at night than day?
Temperature inversion is the reason why sounds can be heard much more clearly over longer distances at night than during the day—an effect often incorrectly attributed to the psychological result of nighttime quiet. … Another example of sound refraction occurs in the ocean.
Can you hear things in space? Space is a vacuum — so it generally doesn’t carry sound waves like air does here on Earth (though some sounds do exist in outer space, we just can’t hear them).
Can sound travel through water Justify your answer?
Answer:Yes ! Sound can travel in water with the speed of 330m/s. We can justify by saying that we can listen to the sounds of dolphins and the large ships inside the water. Some fishes communicate in water through water..
Do whales Echolocate? Echolocation. Toothed whales (including dolphins) have developed a remarkable sensory ability used for locating food and for navigation underwater called echolocation. … The whistles, clicks, groans and other noises made by many toothed whales are also thought to be also important in communication between individuals.
What does a dolphin’s melon do?
That giant forehead on the dolphin is called a melon. And it acts like an acoustic lens, aiding in sound recognition. In addition to the melon, the dolphin’s teeth are arranged in a way that they function like antenna, receiving incoming sound. … So dolphins use echolocation to fill in what they can’t see visually.
Is echolocation a superpower?
Power/Ability to:
The ability to determine the location of objects in the environment by use of reflected sound waves.
How do bats echolocate? Bats navigate and find insect prey using echolocation. The sound waves emitted by bats bounce off objects in their environment. … Then, the sounds return to the bats’ ears, which are finely tuned to recognize their own unique calls.
How far can bats echolocate? The “acoustic field of vision” is the area where the animal can “see” their surroundings using echolocation. A sperm whale can echolocate prey up to 500 meters away, while a bat’s echolocation distance is only 2-10 meters. Bats fly fast and cover approx. one echolocation distance per second.
Do bats scream?
Big brown bats and little brown bats are shouters and produce sounds (if we could hear them) of 110 decibels or similar to the loudness of a smoke alarm. Northern long-eared bats are whispering bats and produce sounds of 60 decibels (similar to the levels of normal human conversation).
What do Megabats eat? Megabats usually eat fruits, and microbats generally eat insects. Some bats have relatively large appetites, such as the Malayan flying fox, which eats about half its body weight every day. But the vampire bat far exceeds even that, eating twice its weight in one day.
Why do Megabats don’t use echolocation?
They tend to be bigger and, with one exception, they don’t use echolocation. They have neither the specialised body parts needed to produce the necessary clicks, nor the genetic signatures that are common to sonar users. Instead, they rely on their large eyes to see at night.
How does bat make sound? Bats navigate and find insect prey using echolocation. They produce sound waves at frequencies above human hearing, called ultrasound. The sound waves emitted by bats bounce off objects in their environment. Then, the sounds return to the bats’ ears, which are finely tuned to recognize their own unique calls.
Can bats hear humans?
Not All Bats Echolocate
Most bat echolocation occurs beyond the range of human hearing. … Some bat sounds humans can hear. The squeaks and squawks that bats make in their roosts or which occur between females and their pups can be detected by human ears, but these noises aren’t considered to be echolocation sounds.
How do shrews Echolocate? Some species of shrews use a series of high-pitched squeaks for echolocation, much as bats do. However, shrews probably use echolocation more for investigating their habitat than for searching out food. Glands located on the hindquarters of shrews have a pungent odor and probably function as sexual attractants.
Do hedgehogs Echolocate?
Which animals use echolocation? Bats, whales, dolphins, a few birds like the nocturnal oilbird and some swiftlets, some shrews and the similar tenrec from Madagascar are all known to echolocate. Another possible candidate is the hedgehog, and incredibly some blind people have also developed the ability to echolocate.
What is echolocation example? Echolocation is what some animals use to locate objects with sound rather than sight. Bats, for example, use echolocation to find food and avoid flying into trees in the dark. Echolocation involves making a sound and determining what objects are nearby based on its echos.
Do’t forget to share this post !