At age 72, at a meeting of the Societé de Biologie in Paris, Brown-Séquard reported that hypodermic injection of a fluid prepared from the testicles of guinea pigs and dogs leads to rejuvenation and prolonged human life. It was known, among scientists, derisively, as the Brown-Séquard Elixir.
Also Who played guitar for Charles Brown? He began a recording and performing career again, under the musical direction of the guitarist Danny Caron, to greater success than he had achieved since the 1950s. Other members of Charles’s touring ensemble included Clifford Solomon on tenor saxophone, Ruth Davies on bass and Gaylord Birch on drums.
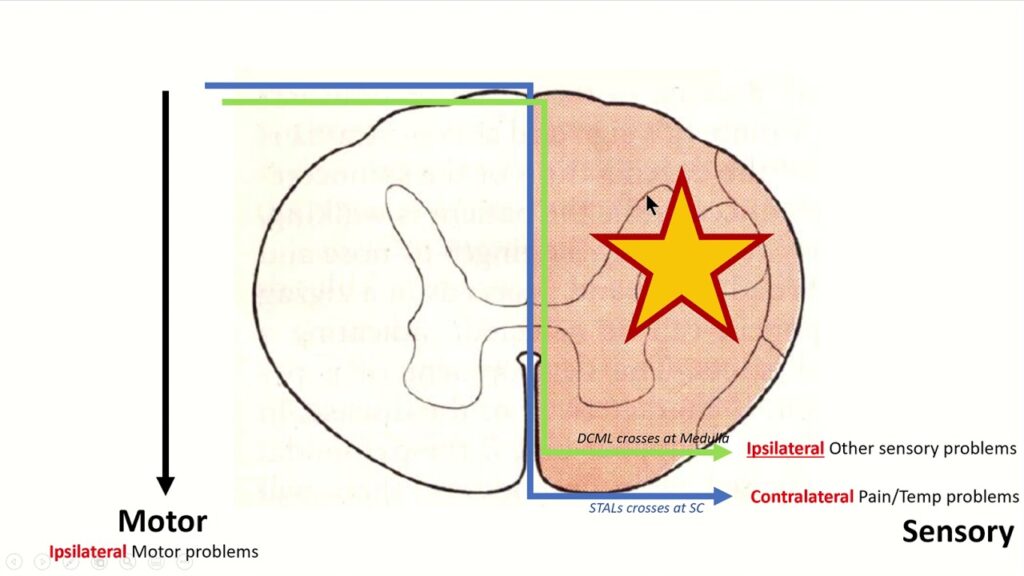
Likewise What is Brown-Séquard syndrome? Brown-Séquard syndrome is a rare spinal disorder that results from an injury to one side of the spinal cord in which the spinal cord is damaged but is not severed completely. It is usually caused by an injury to the spine in the region of the neck or back.
What did Charles Brown-Séquard do? The subject of this fascinating biography was a major player in the evolution of medicine during the 19th century. Charles-Edouard Brown-Séquard is now largely known to medical students and practitioners because of the sensory and motor effects of a transverse spinal cord hemisection, known as Brown-Séquard syndrome.
What is cord syndrome?
Definition. Central cord syndrome is the most common form of incomplete spinal cord injury characterized by impairment in the arms and hands and to a lesser extent in the legs. The brain’s ability to send and receive signals to and from parts of the body below the site of injury is reduced but not entirely blocked.
When did Charles Brown come out? A strip published on April 3, 1971 , suggests he was born around 1963 (setting up the gag that when he is 21, it will be 1984).
…
| Charlie Brown | |
|---|---|
| First appearance | May 30, 1948 (first mention) October 2, 1950 (official debut) |
| Last appearance | February 13, 2000 (comic strip) |
Is clonus a spasticity? Spasticity and clonus result from an upper motor neuron lesion that disinhibits the tendon stretch reflex; however, they are differentiated in the fact that spasticity results in a velocity dependent tightness of muscle whereas clonus results in uncontrollable jerks of the muscle.
Is Brown-Séquard syndrome UMN or LMN? Patients with Brown-Séquard syndrome suffer from ipsilateral upper motor neuron paralysis and loss of proprioception, as well as contralateral loss of pain and temperature sensation.
Who gets autonomic dysreflexia?
Autonomic dysreflexia is a syndrome in which there is a sudden onset of excessively high blood pressure. It is more common in people with spinal cord injuries that involve the thoracic nerves of the spine or above (T6 or above).
What characterizes anterior cord? Anterior cord syndrome is an incomplete cord syndrome that predominantly affects the anterior 2/3 of the spinal cord, characteristically resulting in motor paralysis below the level of the lesion as well as the loss of pain and temperature at and below the level of the lesion.
What was the brown sequard elixir?
Before pitching a game against Boston, Pud used something called the elixir of Brown-Sequard… essentially testosterone drained from the gonads of an animal. And, low and behold, the juiced-up Galvin won.
What is Flavum? One of a series of bands of elastic tissue that runs between the lamina from the axis to the sacrum, the ligamentum flavum connects the laminae and fuses with the facet joint capsules. … The ligament can become a substantial contributor to spinal stenosis, and is usually removed during a lumbar decompression surgery.
What is hyperextending your neck?
Hyperextension of the neck is an injury caused by an abrupt forward then backward movement of the head and neck. This injury is also known as whiplash because the sudden movement resembles the motion of a cracking whip.
What is the Spinothalamic tract?
The spinothalamic tract is a collection of neurons that carries information to the brain about pain, temperature, itch, and general or light touch sensations. The pathway starts with sensory neurons that synapse in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord.
Who did Charlie Brown marry? Peggy Jean is a minor female character in the Peanuts comic strip by Charles M. Schulz. She was the girlfriend of Charlie Brown for many years in the 1990s.
…
Who did Charlie Brown marry?
| Peppermint Patty | |
|---|---|
| Full name | Patricia Reichardt |
| Gender | Female |
Why does Charlie Brown have no hair? Charlie Brown is drawn with only a small curl of hair at the front of his head, and a little in the back. Though this is often interpreted as him being bald, Charles M. Schulz claimed that he saw Charlie Brown as having hair that was so light, and cut so short, that it could not be seen very easily.
Is Charlie Brown based on a true story?
The real Charlie Brown is Charlie Francis Brown, a sandy-haired 53-year-old bachelor who once was accused of sassing a policeman because he gave his name as Charlie Brown. … Schulz lives in Santa Rosa, Calif., but in 1951, both he and Charlie Brown were instructors at Art Instruction Schools, Minneapolis.
Do babies have clonus? Clonus can be physiologic, for instance, term infants can be hyperreflexic, and a few beats of clonus can be a normal finding in this population; however, most infants will not exhibit this finding, and most infants who will go on to demonstrate cerebral palsy will not exhibit clonus.
What causes positive Hoffman’s?
A positive Hoffmann’s sign is suggestive of corticospinal tract dysfunction localized to the cervical segments of the spinal cord. In this regard, it is analogous to the Babinski sign. Conditions such as multiple sclerosis, hyperthyroidism, and anxiety will also result in a positive sign.
What is the difference between clonus and myoclonus? Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Myoclonus is a brief, involuntary, irregular (lacking rhythm) twitching of a muscle or a group of muscles, different from clonus, which is rhythmic or regular. Myoclonus describes a medical sign and, generally, is not a diagnosis of a disease.
What is sacral sparing?
What Does Sacral Sparing Indicate? Sacral sparing is used to help diagnose whether a person’s spinal cord injury is complete or incomplete. With complete spinal cord injuries, all sensory and motor functions below your level of injury are affected because signals from the brain cannot travel past the spinal lesion.
Which spinal tract is for light touch? The anterior spinothalamic tract transmits light touch. Autonomic function traverses within the anterior interomedial tract. Sympathetic nervous system fibers exit the spinal cord between C7 and L1, whereas parasympathetic system pathways exit between S2 and S4.
What is transection of spinal cord?
Spinal cord transection refers to a tear within the spinal cord as a result of a significant traumatic injury. The degree of neurological compromise corresponds with the degree of cord transection.
Do’t forget to share this post !