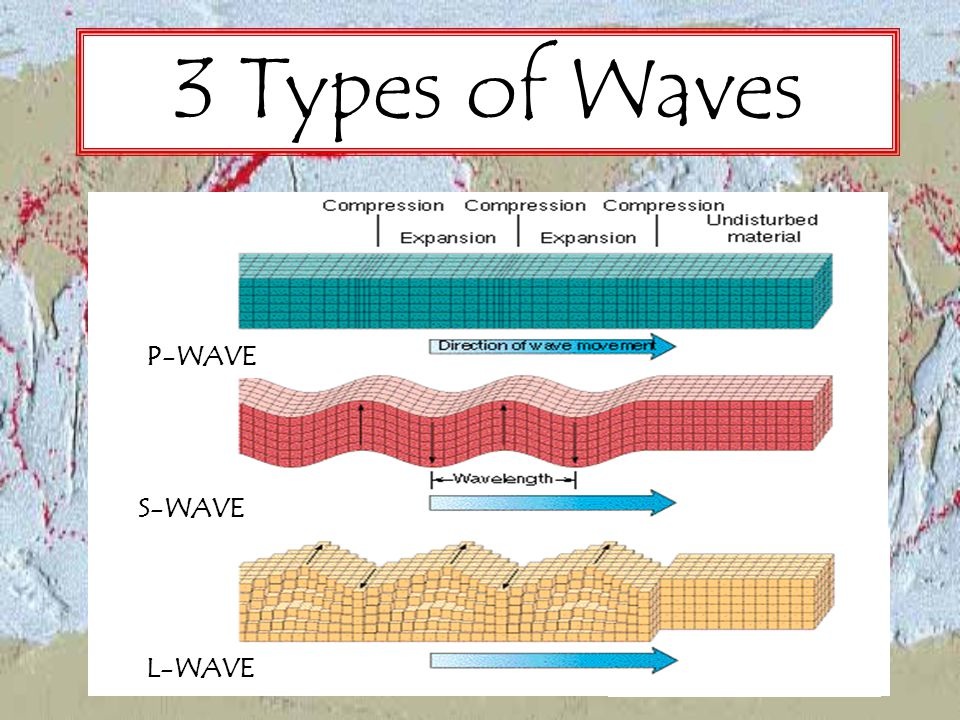
P-waves. P-waves, also known as primary waves or pressure waves, travel at the greatest velocity through the Earth. When they travel through air, they take the form of sound waves – they travel at the speed of sound (330 ms–1) through air but may travel at 5000 ms–1 in granite.
Also What is primary waves and secondary waves? The P-wave (primary or pressure wave) is a pulse of energy that travels quickly through the earth and through liquids. … The S-wave (secondary or shear wave) follows more slowly, with a swaying, rolling motion that shakes the ground back and forth perpendicular to the direction of the wave.
Likewise What is the meaning of secondary waves? A type of seismic body wave in which rock particles vibrate at right angles to the direction of wave travel. Secondary waves cause the rocks they pass through to change in shape. … Also called shear wave S wave See Note at earthquake.
How is primary wave related to secondary wave? Primary waves, also known as P waves or pressure waves, are longitudinal compression waves similar to the motion of a slinky (SF Fig. … The motion of secondary waves is perpendicular to the direction of the wave travel, similar to the motion of vigorously shaking a rope (SF Fig.
What do Primary waves do?
The first set of waves to be detected by seismographs are P waves, or primary waves, as they’re the fastest. They’re compressional or longitudinal waves that push and pull the ground in the direction the wave is traveling. They usually cause very little damage.
Are secondary waves transverse or longitudinal? S-waves are transverse body waves and thus can only be propagated within solid bodies such as rocks. P-waves are longitudinal waves similar to sound waves; they propagate at the speed of sound and have large ranges.
What are primary waves in simple words? A P wave (primary wave or pressure wave) is one of the two main types of elastic body waves, called seismic waves in seismology. P waves travel faster than other seismic waves and hence are the first signal from an earthquake to arrive at any affected location or at a seismograph.
Are S waves secondary waves? S waves are called secondary waves because they always arrive after P waves at seismic recording stations. Unlike P waves, S waves can travel only through solid materials. After both P and S waves have moved through the body of Earth, they are followed by surface waves, which travel along Earth’s surface.
What are surface or L waves?
Surface waves, in this mechanical sense, are commonly known as either Love waves (L waves) or Rayleigh waves. A seismic wave is a wave that travels through the Earth, often as the result of an earthquake or explosion. … Surface waves can travel around the globe many times from the largest earthquakes.
Is Primary Wave also known as transverse wave? A disturbance like an earthquake at any point on the Earth will produce energetic waves called seismic waves. … For seismic waves through the bulk material the longitudinal or compressional waves are called P waves (for “primary” waves) whereas the transverse waves are callled S waves (“secondary” waves).
What type of wave is a secondary wave?
S waves are seismic body waves meaning they travel through the Earth’s interior. Their velocity is slower than that of P waves, and they are normally the second major phase to be observed on a seismogram, and are therefore also referred to as secondary waves.
What are the main features of primary waves? Primary Waves are compressional which means they move through (compress) a solid or liquid by pushing or pulling similar to the way sound travels through the air. The particles of the material a P Wave pushes through move in the direction of the Primary wave’s energy. This is called the direction of wave propagation.
What cause more damage Love or Rayleigh waves?
Love waves cause more damage than Rayleigh waves, but both are highly destructive because they occur near the surface of the Earth.
What causes primary waves?
There are three types of waves that are created when stress is released as energy in earthquakes: P, S, and surface waves. The P wave, or primary wave, is the fastest of the three waves and the first detected by seismographs. They are able to move through both liquid and solid rock.
Why do P waves come first? P waves travel fastest and are the first to arrive from the earthquake. In S or shear waves, rock oscillates perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. … The direct P wave arrives first because its path is through the higher speed, dense rocks deeper in the earth.
Are body waves longitudinal? When seismic waves are first created, they travel outwards in all direction from their source. Body waves travel through the interior of the earth, and have two main types: P-Waves (Primary waves) are Longitudinal Waves. S-Waves (Secondary waves) are Transverse Waves.
Why are P waves called primary waves?
P waves cause the ground to compress and expand, that is, to move back and forth, in the direction of travel. They are called primary waves because they are the first type of wave to arrive at seismic recording stations.
Which best describes a primary wave? Primary waves are alternatingly compressional and extensional, and cause the rocks they pass through to change in volume. These waves are the fastest traveling seismic waves and can travel through solids, liquids, and gases.
What is another name of primary wave?
A P wave, or compressional wave, is a seismic body wave that shakes the ground back and forth in the same direction and the opposite direction as the direction the wave is moving.
How do primary waves move? Primary (compressional) waves
They travel through the Earth’s interior and can pass through both solid and molten rock. They shake the ground back and forth – like a Slinky – in their travel direction, but do little damage as they only move buildings up and down.
Are seismic S waves longitudinal?
There are two types of seismic waves: P-waves, which are longitudinal waves. S-waves, which are transverse waves.
Do P-waves come first? P waves travel fastest and are the first to arrive from the earthquake. In S or shear waves, rock oscillates perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. In rock, S waves generally travel about 60% the speed of P waves, and the S wave always arrives after the P wave.
What is Al wave?
noun Geology. an earthquake wave that travels around the earth’s surface and is usually the third conspicuous wave to reach a seismograph. Also called long wave .
What are the 3 types of seismic wave? There are three major kinds of seismic waves: P, S, and surface waves. P and S waves together are sometimes called body waves because they can travel through the body of the earth, and are not trapped near the surface. A P wave is a sound wave traveling through rock.
Do’t forget to share this post !